What We Do
Our Vision
Medical science is evolving very fast and so is the technology in medical sciences. With the incorporation of newer technologies in medical field, the management of patients is becoming more and more accurate and predictable. This is particularly important in surgical specialties. We are a group of professionals with experts from different fields of medical and engineering. Our vision is to incorporate & apply newer technologies in medical field to facilitate the work of medical experts, so that the treatment become more and more accurate and predictable.
How it looks
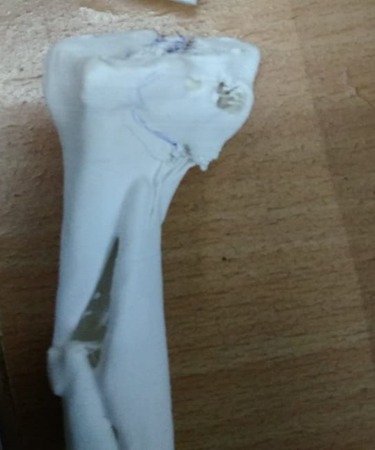
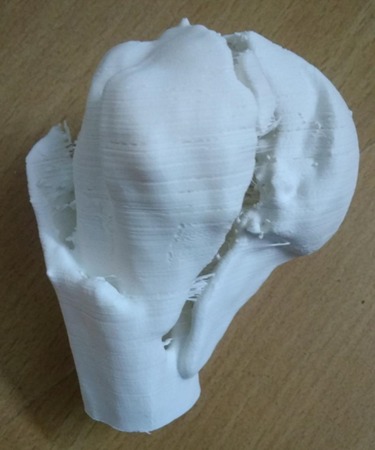
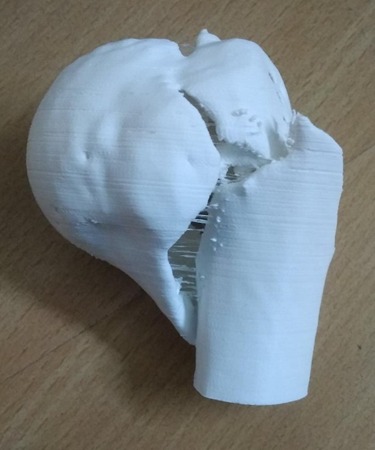
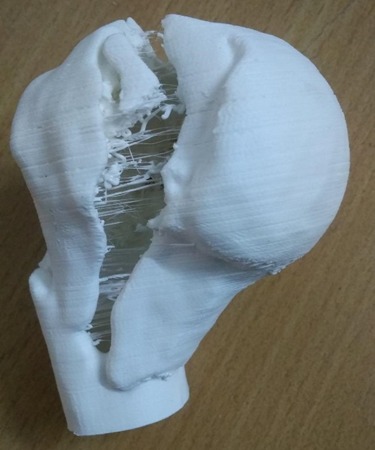
3D MODEL
How We Do It
The Technique
DESIGN
3-D printing is a recently developed technology, that creates solid models from various formats of 3-D image files, which includes CT Scans & MRIs. In this technique, the digital image file (commonly DICOM file) is converted to a digital 3-D model file (commonly STL file) which is readable by the 3-D printer.
PRINTING MODEL
This 3-D printer then creates a model replica from the 3-D model file by a process called additive manufacturing. There are many types of 3-D printers available in the market. But one which is commonly used in orthopaedic trauma surgery is PLA (poly lactic acid) printer.
MATERIAL
PLA is a plastic material that melts at high temperature and quickly hardens, once the temperature is reduced. In this printer, a PLA wire roll is attached to a thin nozzle. The nozzle can move in all three dimensions on a glass platform. This nozzle also has a heating system in it.
THE PROCESS
During printing, this nozzle is heated, and this PLA wire is dropped from the nozzle on the glass platform. This PLA material is quickly dried up and hardened. The nozzle keeps on moving on the glass platform as per the 3-D image file and keeps on adding PLA material bit by bit / layer by layer on the glass platform and a model replica is so created.
SCAN TO 3D
This technology is being used widely in designing industry. Its use in medical field is also gaining momentum. In medical science, we create solid models from 3-D CT Scans or MRIs, which replicate the same morphology as the CT / MRI of that body part.
THE SCOPE
Presently this technique is being used in dental surgery and complex tumor surgeries and its use in trauma surgery is also increasing as making bone models is comparatively easy and more accurate.
3D CT vs 3D Model
APPLICATION
Fracture is a break in continuity of a bone. Usually, it can easily be diagnosed by plain X-Rays. These Plain X-Rays give sufficient knowledge about fracture anatomy, displacement of main fragments etc. but in complex fractures like juxta-articular fractures or fractures involving the articular surfaces, they fail to provide us the necessary information regarding the degree of communition.
The exact extent of articular extension of fracture lines & orientation of fracture fragments, which is very much necessary to achieve anatomical alignment during fracture fixation. As more and more fractures are being treated surgically by internal fixation, a better understanding of fracture geometry is required to plan the surgical procedure to achieve an exact anatomical alignment.
CT Scan is being used for quite some time as the main diagnostic tool to provide such information to the surgeon in complex juxta-articular & intra-articular fractures. With the availability of modern 64 slice or 128 slice CT-Scanners and advanced 3-D reconstruction software, it is possible to create a 3-D picture of the fracture.
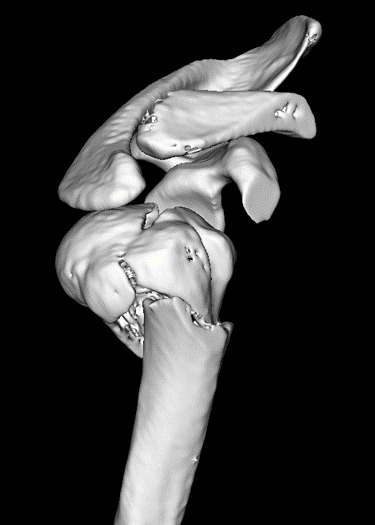
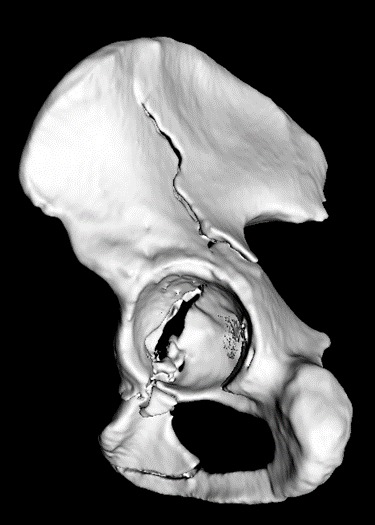
These 3-D pictures provide a very good understanding of fracture geometry. Although 3-D CT-Scan is being used routinely now a days to analyse complex fractures but sometimes it fails to provide exact understanding of fracture geometry. In a 3-D CT scan, 3-D reconstructed images are presented to the surgeon in 2-D image format.
So he has to use a lot of imagination in order to have a clear 3-D picture of fracture geometry in his mind. The technique of creating 3-D model, can give the surgeon a better chance to understand the three-dimensional geometry of the fracture so that he can reduce and fix the fracture more accurately.
As these models are made in true dimensions, contouring of plates, measurement of screw size can be done preoperatively. In addition, these models are autoclavable, so they can be autoclaved and kept on table during surgery for reference. Moreover, These 3D models also give a chance to the surgeon to have a tactile feeling of the fractured part.
Why Use It
THE BENEFITS
The main use of this technique is in management of complex intra articular fractures, where understanding of fracture geometry is the key to reduce and fix the fracture surgically. A 3-D model of the fracture provides the surgeon a better chance to understand the exact fracture configuration. At the same time the surgeon can explain the severity of the fracture to the patient and attendant in a better way.
We can very well assume that if the surgeon has a clear image of fracture geometry in his mind while operating, the fracture reduction and fixation will be easier and more accurate.
If the fracture reduction & fixation is accurate, the outcome of surgery would be more favourable for the patient.
How it works
THE GALLERY
MODEL/ SIZE | EXAMPLE | CHARGES | Inaugural Offer @ 50% (Till 31st October 2023) |
Small (Size up to 3” * 3”) | Lower end Radius | 4000/- | 2000/- |
Medium (Size up to 5” * 5”) | Proximal or Distal Tibia | 6000/- | 3000/- |
Large (Size up to 9” * 9”) | Acetabulum / hemipelvis | 8000/- | 4000/- |
Extra large/ Special | Pelvis | To be decided on case to case basis |
How to reach us
CONTACT US
Please fill the form below to get more information regarding our services or contact us. All fields in this form are mandatory.